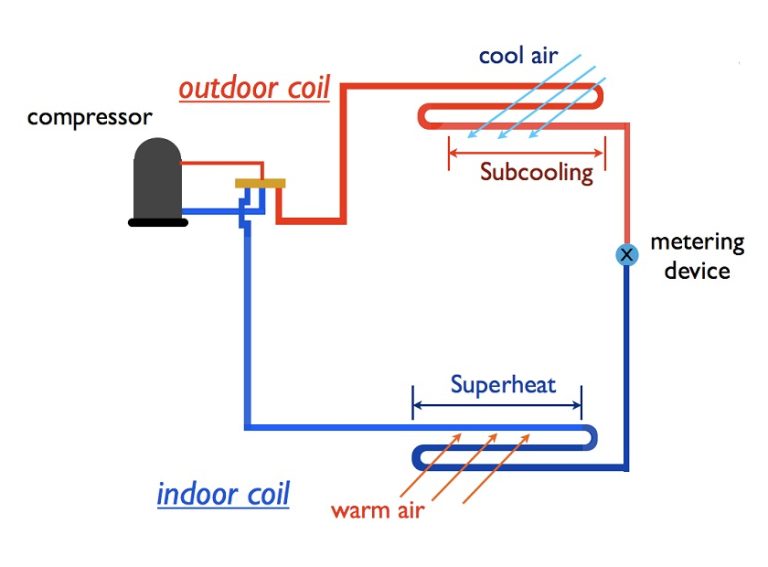
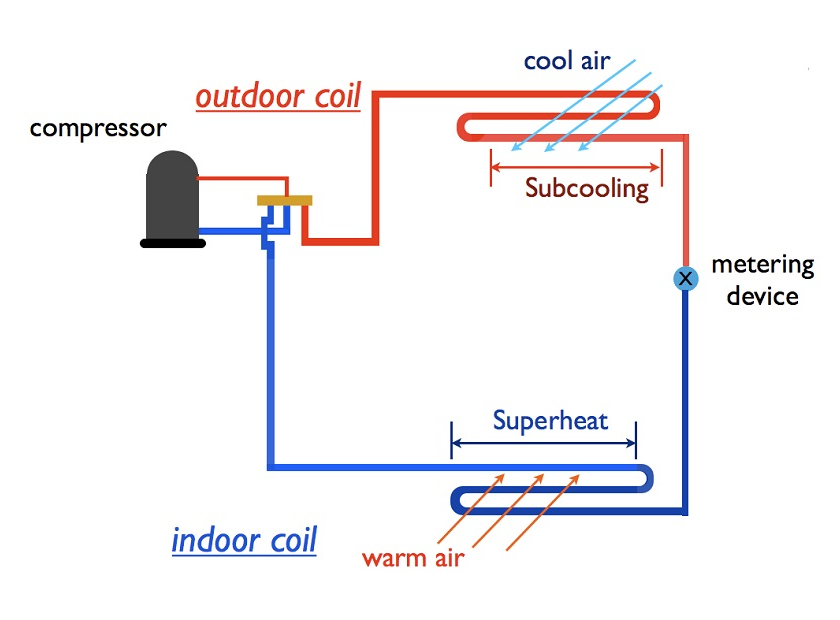
Ensuring a healthy indoor environment calls for smart building maintenance strategies. It’s important to look beyond a single system or method and focus on the four key phases of planned maintenance. So, what exactly are these phases? By diving into this topic, you can create more effective and efficient building maintenance practices that stand out.
What Are the 4 Phases of Planned Maintenance HVAC?
Planned maintenance can be categorized in many ways but most commonly falls into four categories:
• Corrective maintenance
• Preventive maintenance
• Risk-based maintenance
• Predictive maintenance
In the realm of building maintenance, a well-rounded approach is key to achieving optimal speed and performance over time. Savvy maintenance teams blend the strengths of different maintenance strategies to create a comprehensive plan tailored to each building’s needs. Here’s abreakdown of the four key maintenance phases and how they contribute to a robust maintenance strategy

Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance takes place when repairs are needed. It can be reactive, fixing equipment after it breaks down, known as run-to-failure maintenance. Alternatively, it may follow scheduled inspections that identify issues needing attention. Corrective maintenance offers several advantages
• Allows personnel to focus on other tasks until issues arise
• Costs are only incurred when failures occur
• Requires minimal planning
Corrective maintenance is best applied to non-critical assets that can be fixed or replaced easilyand inexpensively, or in systems with redundancies that prevent complete failures. However, this approach should not be the main component of any maintenance plan.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance aims to proactively address potential issues before they cause downtime. This phase can take different forms:
• Time-based: Scheduled inspections at regular intervals to spot maintenance needs
• Usage-based: Maintenance based on equipment usage metrics, like hours operated or production cycles completed
• Condition-based: Monitoring assets to determine when maintenance is necessary
Corrective maintenance is best applied to non-critical assets that can be fixed or replaced easilyand inexpensively, or in systems with redundancies that prevent complete failures. However, this approach should not be the main component of any maintenance plan.
Preventive maintenance offers notable benefits:
• Reduces downtime and equipment failures
• Lowers the frequency of major repairs and replacements
• Extends the lifespan of equipment and systems
• Optimizes maintenance staff workload, reducing overtime and major repair-related costs
Despite these advantages, preventive maintenance can be debated due to its costs and labor demands. Weighing emergency repair expenses against preventive maintenance costs is crucial for efficient resource use
Read more about how to clean reusable HVAC Filter!
Risk-based Maintenance
Risk-based maintenance focuses on analyzing potential events, from minor repairs to severe failures, to prioritize maintenance activities. It involves:
These platforms continuously monitor equipment and conditions, using machine learning
algorithms to detect anomalies before they become apparent to occupants or staff. Over time,
they improve their predictions regarding future maintenance needs, ensuring a healthy indoor
environment.
By understanding risks, stakeholders can create targeted plans to handle diverse maintenance situations
Predictive Maintenance
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has revolutionized maintenance planning. IoT devices collect valuable data that helps facility managers detect issues early and address them swiftly. In conjunction with smart building platforms, this data fuels predictive maintenance.
These platforms continuously monitor equipment and conditions, using machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies before they become apparent to occupants or staff. Over time, they improve their predictions regarding future maintenance needs, ensuring a healthy indoor environment.
The advantages of predictive maintenance include:
• Reduced risk of major malfunctions
• Early problem detection leading to simpler fixes
• Minimal downtime
• Cost reduction
• Enhanced occupant safety and experience
• Efficient allocation of maintenance resources
• Simplified budgeting
Predictive maintenance is a vital component that enhances the effectiveness of the other maintenance phases, leading to a more strategic approach to maintaining healthy buildings. By integrating these phases, stakeholders can devise a comprehensive strategy that maximizes building performance and longevity.
Finding the Right Tools
Instead of simply asking, “What are the 4 phases of planned maintenance?” it’s crucial to explore, “What are the best tools to build a strong maintenance strategy?”
Effective maintenance strategies depend heavily on advanced technology. Selecting a cuttingedge building platform equipped to handle predictive maintenance, precisely evaluate risks, and facilitate data-driven decisions is vital. By utilizing a state-of-the-art platform, you can leverage data to revolutionize your maintenance program and enhance your building’s health
FAQs
1. How does predictive maintenance work?
Predictive maintenance uses data collection and analysis to anticipate when equipment or systems may need maintenance, allowing for proactive measures to be taken before any major issues arise.
2. What are the benefits of implementing predictive maintenance in buildings?
• Reduced risk of major malfunctions
• Early problem detection leading to simpler fixes
• Minimal downtime
• Cost reduction
• Enhanced occupant safety and experience
• Efficient allocation of maintenance resources
• Simplified budgeting
3. Can any building implement a predictive maintenance program?
Yes, any building can implement a predictive maintenance program, as long as it has the necessary technology and data collection capabilities in place. It is important to consult with experts and identify the right tools for your specific building’s needs.
4. What is the role of data in maintenance strategies?
Data plays a crucial role in maintenance strategies as it allows for informed decision-making, proactive problem solving, and efficient resource allocation. Without data, it can be challenging to identify potential issues and make well-informed decisions about maintenance practices. Overall, leveraging technology and utilizing data-driven solutions can greatly improve the effectiveness of planned maintenance strategies in buildings. So instead of just focusing on the phases, it’s important to also consider the tools and resources needed for successful implementation. This will ultimately lead to healthier buildings, cost savings, and improved occupant experience
5. How can building managers use predictive maintenance to improve energy efficiency?
Predictive maintenance can help building managers identify potential energy inefficiencies early on, allowing for targeted repairs and replacements to be made before they result in higher utility costs. By continuously monitoring equipment and systems, building managers can also collect data on energy usage patterns and make data-driven decisions on ways to optimize energy
consumption. This can lead to significant cost savings and a more sustainable operation of the building
6. Are there any drawbacks to implementing predictive maintenance in buildings?
Some potential drawbacks of implementing predictive maintenance include the initial investment in technology and data collection tools, as well as the need for specialized training for staff members responsible for maintaining the building. Additionally, integrating predictive maintenance practices may require changes to existing maintenance schedules and procedures, which can disrupt daily operations. However, these potential challenges can be overcome by carefully planning and implementing a well-executed strategy.