If you’re aiming to maintain a comfortable home environment all year round, you’ve likely encountered the terms HVAC and AC. But what exactly do they mean, and how are they distinct?
Let's explore the differences between HVAC and AC!
HVAC vs AC
The primary distinction between HVAC and AC is that HVAC encompasses the entire system responsible for heating, cooling, and ventilation in a building. In contrast, AC typically refers to systems specifically focused on cooling. Essentially, air conditioning is a component of an HVAC system.

What is HVAC?
What is an AC system?
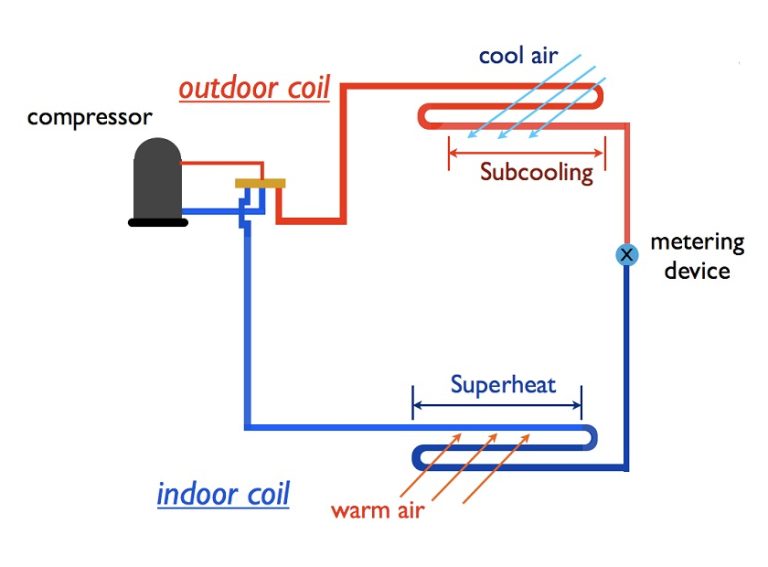
AC stands for air conditioning
and its role is to cool indoor air by removing heat and moisture. A typical central air conditioning setup includes:
What Types of Air Conditioners are There?
Air conditioners operate independently of a furnace and don’t utilize ducts. There are primarily two types;
Window Unit
These popular air conditioners, available in various sizes, are designed to cool one room or a larger space. They became widely used in the 1950s as an affordable cooling solution. While they provide some relief from heat, they aren’t the most energy-efficient, can damage window frames, and may not be aesthetically pleasing. Temperature regulation can also be challenging with window units
Ductless or Split Systems
These systems are useful where ductwork is limited, consisting of an indoor unit that blows cold air and an outdoor unit that generates it. Though not as efficient as a full HVAC system, they are often a better choice than window units. Their compact size might make them a viable alternative to an HVAC setup
What Are The Benefits And Drawbacks Of HVAC And AC Systems?
When deciding between HVAC and AC systems, understanding their respective advantages and disadvantages is key. Here’s what you should consider:
1. Comfort
HVAC systems offer comprehensive comfort, providing both heating and cooling, making them adaptable to any weather changes. You can easily customize the temperature settings to suit yourneeds all year round. In contrast, AC systems are designed solely for cooling, which might leave you needing an additional heating solution in colder months. Additionally, central ACs are typically part of HVAC systems, meaning they can’t be installed independently
2. Energy Efficiency
HVAC systems can outperform AC systems in energy efficiency when equipped with advanced features such as variable speed motors, programmable thermostats, and zoning controls. These features allow you to optimize energy use based on different zones and seasons. On the other hand, AC systems can also be energy efficient if they boast high SEER ratings and Energy Star certification, indicating their cooling efficiency per unit of electricity. If you reside in a hot climate, focusing solely on AC might suffice
3. Cost
Initially, HVAC systems might require a larger investment than standalone AC units due to the complexity of installation and maintenance. However, they can offer long-term savings through energy efficiency and an increase in property value. AC systems, meanwhile, are generally less expensive upfront and may incur lower repair costs. It’s crucial to assess your home’s specific needs—for instance, multiple mini-split ACs could end up being costlier than a comprehensive HVAC system. Consulting a reputable HVAC expert before making a choice is advisable.
4. Space

Environmental Impact
The Difference Between HVAC and AC